Frequency Divider & Counters

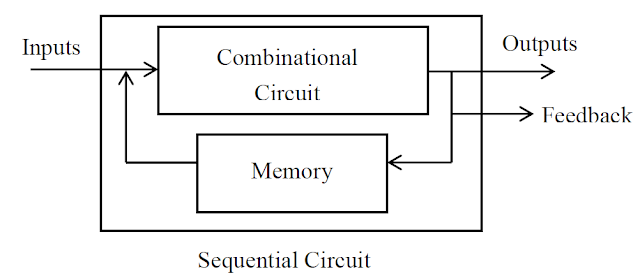
Frequency Divider A frequency divider can be constructed from J-K flip-flops by taking the output of one cell to the clock input of the next. The J and K inputs of each flip-flop are set to 1 to produce a toggle at each cycle of the clock input. For each two toggles of the first cell, a toggle is produced in the second cell, so its output is at half the frequency of the first. The output of the fourth cell is 1/16 the clock frequency. The same device is useful as a binary counter. Simulation of Frequency Divider Counters A counting circuit composed of memory elements, such as flip-flops and electronic gates, is the simplest form of sequential circuit available. All sequential circuits are of two types, synchronous (clock driven) asynchronous (event driven) In synchronous circuits, changes in the circuit state are synchronised to the normally periodic clock pulses, whereas in event driven circuits state changes are governed by events such as, for example, the occur...